Week 6:Electronics Design
Milling a PCB
This week we focused on PCB ( printed circuit board) manufacturing, PCBs are good for preventing short circuits and are a good way for milling non toxic materials. The PCB is a milled sheet of copper that has pads and signal trace structures from a digital circuit board, also known as a a lay out file. In the Fab Lab Barcelona facilities, we have access to the The Roland monoFab SRM-20
Most common materials used for milling are phenolic resin, epoxy resin, and polyester resin. We learnt how to solder a line for LED lights on a pre-cut PCB board.
Soldering a PCB Board. Soldering is a process in which two or more items are joined together by melting and putting a filler metal into the joint,
the filler metal having a lower melting point than the adjoining metal.
How to solder:
Clean the soldering surface
Turn on the soldering iron and set the melting point of the solder
Hold the tip of the leand and contact point
Touch the solder wire to the contact pint until it flows around the lead
Make sure there is coverage of the contact area, forming a slight pyramid shape
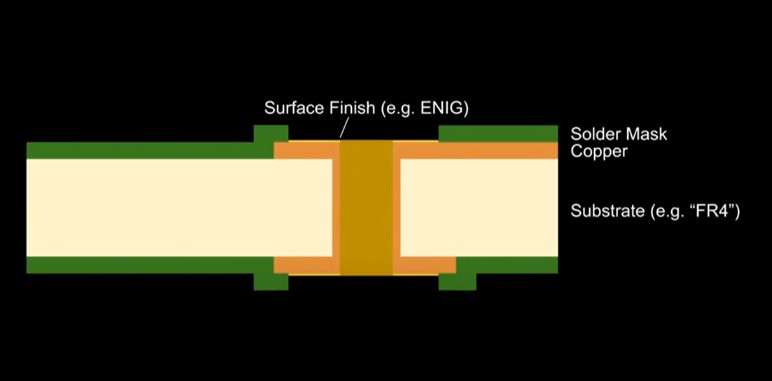
Cross section of a PCB
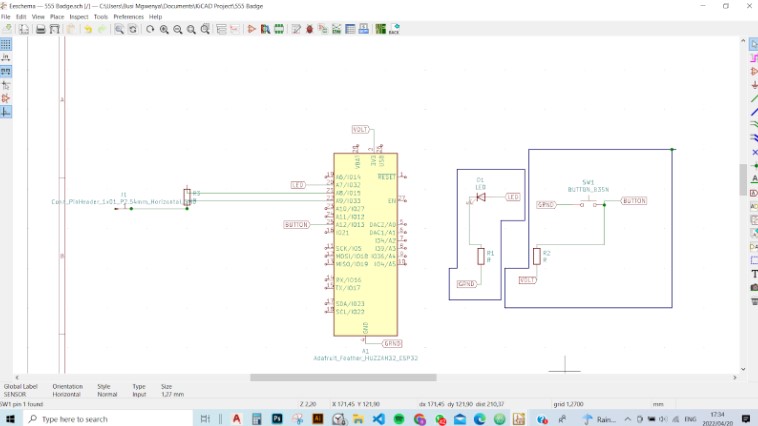
Steps I followed to design the PCB
Step 1: Firstly, I drew the schematic for a button and led Light. I First thought I would
like to use a capacitative sensor, with the help of a classmate I drew the schematic, but I decided not to use it at the end.
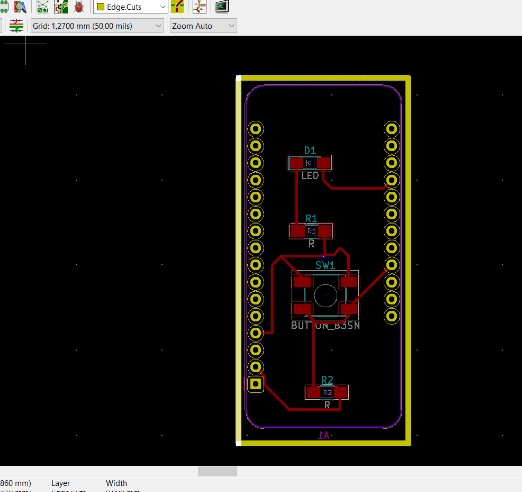
Step 2: After drawing the schematic, I saved the file with a .net extension and opened
it in the PCBnew file as a netlist file. There I arranged the components neatly, set the track sizes,
drew the route tracks and then the edge cuts.
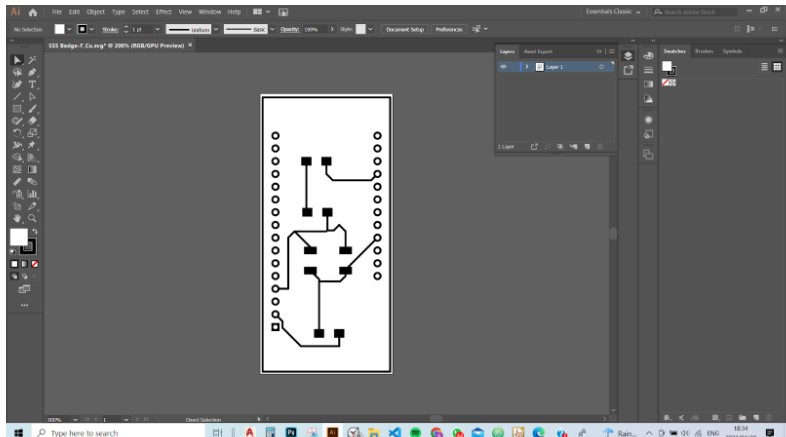
Step 3: The file was then exported to Illustrator, where I configured the line sizes,
then also saved it as a PNG file ready to be milled on LAB LIFE day
Download the KiCAD File here



